Cyber Capacity Building Impact Evaluation
Facilitating Impact Evaluation Efforts for More Resilient Development
Overview
Within the global Cybersecurity Capacity Building (CCB) community there is a growing demand for more systematised evaluation practices that improve CCB program design, delivery and outcomes. Underdeveloped evaluation methodologies and inconsistent evaluation implementation are preventing greater evidence informed policy making, impact measurement and cross project analysis. As a result, through open collaboration with the wider community, this project is seeking to develop a scalable framework for CCB evaluations that can be utilised by various stakeholders to accurately measure impact, cultivate a comprehensive evidence base for CCB and improve future project outcomes.
It has been developed in line with the “Accra Call for Cyber Resilient Development” made at the Global Conference on Cyber Capacity Building (GC3B), the global Cybersecurity Capacity Building (CCB) 2023. Within the 'Accra Call', the global CCB community committed to improve the measurement of cyber capacity building results [….] by actively and systematically integrating methodologies and good practices from the international development field”. This work is being completed in support of the Global Forum on Cyber Expertise (GFCE)’s Strategy and Assessments Working Group (GFCE WG).
Project Structure and Delivery
Through continued research and collaboration with the CBB community, the aim of this project is build consensus and consistency on how to assess CCB impact. Preliminary research indicates that there are several factors restricting monitoring and evaluation within CCB. These include a lack of agreement on what CCB interventions and categories exist, who CCB target groups are, what the outcomes and impacts of CCB interventions are expected to be based on their target groups and context, and what data and methods are needed to evaluate specific interventions.
As such, the project has been separated into four areas to holistically address these challenges:

Theory:
The theory section analyses the assumptions of how CCB is expected to work. This includes developing a series of population, intervention and outcome typologies to improve the consistency through which CCB policies are defined and explained; conducting a systematic review of the literature on evidence evaluation in CCB; and documenting the theories of change informing CCB activities.
When finalised, this section will produce a toolkit of high-level theory of change models covering the breadth of potential CCB interventions. More detailed examples of 2-3 common interventions will also be published to demonstrate an in-depth working of the theory model.
Data:
After building consensus on what CCB evaluation evidence exists and how policies and programmes are expected to work, the project will investigate the availability, quality and suitability of different data sources for evaluating CCB interventions. A range of data and measurement tools already exist to support the evaluation of theories of change in this field, however, it is unclear which data and measurement tools should be used for which intervention. Consequently, within this section, the project will work to identify which measures work best for which interventions and provide greater clarity on what data is suitable for measure outcomes and impacts in certain circumstances. In doing so it seeks to contribute to the consistent use of data in monitoring and evaluation within the CCB community, while also identifying existing data gaps that coordination to address.
Methodology:
After identifying which data is suitable for which intervention, the project will then develop research and guidance on which evaluation methods are best suited for different CCB interventions and contexts. A variety of evaluation methods exist to assess policies and programs, but there is limited understanding of when certain methods are more or less likely to produce useful, valid, credible, and timely insights of CCB interventions. This section will help build consensus on the most appropriate evaluation approaches to use for each intervention type in a given context and at a certain scale.
Use:
The final stage of the project will provide use cases of CCB impact evaluations using the developed process to illustrate the benefits of consistent, consensus based evaluations. These will be used to advocate for further investment in CCB evaluation.
For further details what our vision is for each of the areas, how we want to achieve it, and what the specific outputs, please read the concept note:
Objectives
Taken together, the aim of the combined project sections is to help:
- Accurately attribute outputs and outcomes of CCB to impacts,
- Align CCB interventions with international development program requirements to improve cooperation and boost cross-sector investment, and
- Facilitate more targeted CCB investments, interventions and research.
In doing so, the project will:
- Assist government to better understand what to prioritise and where to invest,
- Allow funders to assess the impacts of their investments and improve their programs,
- Enable implementors to review the effectiveness of their implementation processes, and
- Equip researchers with accurate data that can inform better research and policy making.
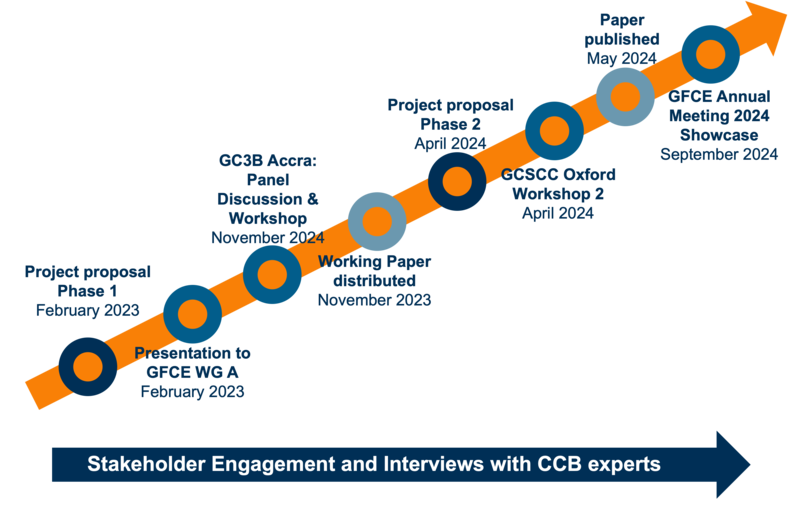
Progress and Publications
The project started with two sessions at the GC3B: A panel discussion “Driving impact: making the case for better evaluation of CCB”, making the case for CCB actors to invest resources in IE; and a complementing practitioner workshop “Improving CCB Evaluation Practice - Knowledge Sharing and Community Building”. In both sessions, members of the CCB and International Development (ID) communities identified the strong need for more knowledge, research, and action on what works and doesn’t work in CCB and on what the solutions could be. The session outcomes are summarised here.
We co-authored a paper “Evaluating the Impact of Cybersecurity Capacity Building” which provides the community members with a problem statement and outline of potential pathways for solutions.
Partners
This research is undertaken by the GCSCC, Integrity and Royal Holloway University London (RHUL) and in collaboration with members of the CCB and ID communities.
This research work is being undertaken in support of the GFCE WG and in collaboration with members of the CCB and ID communities.
Call to Action
It is unlikely that all the proposed outputs of this work can be delivered without material and/or financial contribution from other stakeholders. The project team has started to establish how the work can be scaled up and down and seeking to secure sufficient resources to take the minimum feasible level of work forward.
If you’re are interesting in getting involved and receive updates the project’s process please write to carolin.weisser@cs.ox.ac.uk



